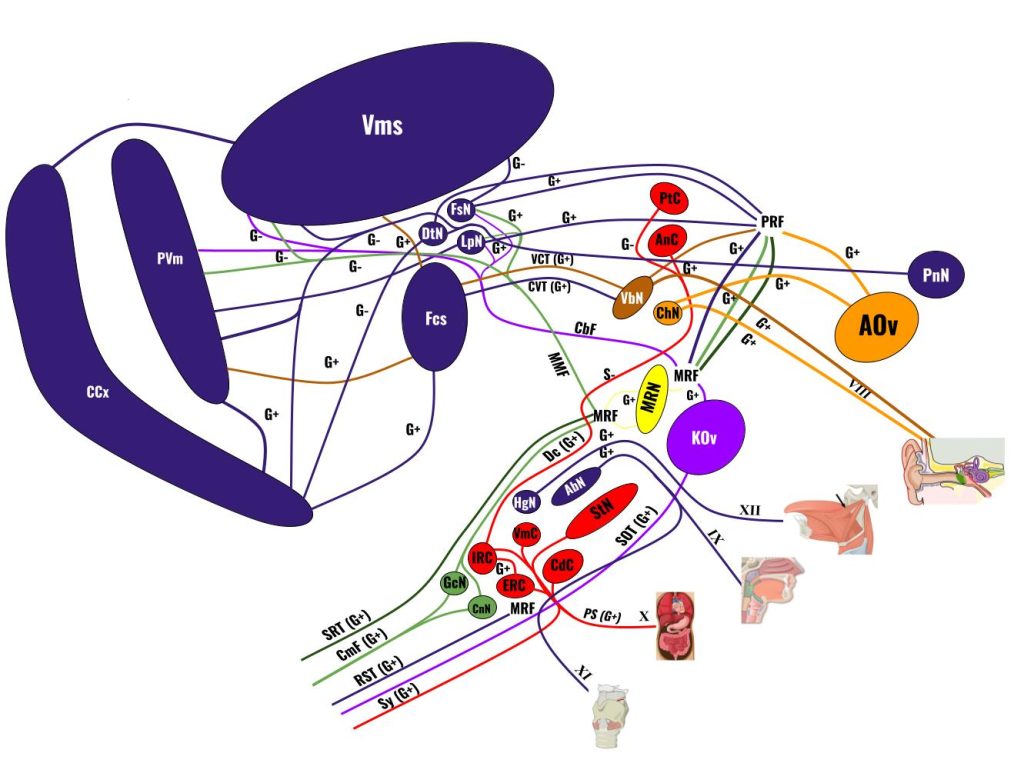
Despite its very complex appearance, this is a grosely simplified model of the neural circuitry of the rhombencephalon (medulla oblongata, pons and cerebellum). The largest simplification is that done to the neural circuitry surrounding the reticular formation which is not fully or even partially understood. Some notable nerual circuits that can be seen on this graphic are that of the medullary vital nuclei, cerebellum and the pontine breathing centers.
Key:
Neurotransmitters:
- G+ Glutamate
- G- GABA
- A+ Acetylcholine
- S- Serotonin
- N+ Noradrenaline
- D+ Dopamine
- E- Endorphins
Cranial Nerves:
- XII: Hypoglossal Motor Nerve
- XI: Accessory Motor Nerve
- X: Vagus Motor and Sensory Nerve
- IX: Glossopharyngeal Motor and Sensory Nerve
- VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory Nerve
Tracts:
- SRT: Spinoreticular Tract
- CmF: Columnar Fasciculi
- RST: Reticulospinal Tract
- SOT: Spino-olivary Tract
- Sy: Sympathetic
- PS: Parasympathetic
- Dc: Decussation
- MMF: Medullary Mossy Fibers
- CbF: Climbing Fibers
- VCT: Vestibulocerebellar Tract
- CVT: Cerebellovestibular Tract
- PMF: Pontine Mossy Fibers
- VST: Vestibulospinal Tract
Nuclei
- CnN: Cuneate Nucleus
- GrN: Gracile Nucleus
- IRC: Inspiratory Respiratoty Center
- ERC: Expiratory Respiratory Center
- CdC: Cardiac Center
- VmC: Vomiting Center
- StN: Solitary Nucleus
- HgN: Hypoglossal Nucleus
- AbN: Ambiguus Nucleus
- KOv: Kinesthetic Olive
- MRN: Medulary Raphe Nuclei
- AnC: Apneustic Center
- PtC: Pneumotaxic Center
- ChN: Cochlear Nucleus
- VbN: Vestibular Nucleus
- Fcs: Flocculus
- Vms: Vermis
- PVm: Paravermis
- CCx: Cerebellar Cortex
- IpN: Interposed Nucleus
- DtN: Dentate Nucleus
- FsN: Fastigial Nucleus
- PnN: Pontine Nucleus
Colors:
- Dark Green: Gross Touch
- Green: Fine Touch
- Blue: Kinesthesia
- Dark Orange: Vestibular Sense
- Orange: Audition
- Red: Autonomic Motor
- Purple: Somatic Motor
- Yellow: Neurotransmitter-Specific Signals